The Comprehensive Guide to Pregnancy: From Conception to Birth and Beyond

Pregnancy is a complex physiological process that involves significant changes in a woman's body to support the growth and development of a new life. This guide aims to provide a detailed, scientifically accurate overview of pregnancy, from conception to postpartum care, including critical information on maintaining maternal and fetal health.
I. The Biology of Conception
A. Ovulation and Fertilization
Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. During this process:
- The ovary releases a mature egg (oocyte) into the fallopian tube.
- Sperm must reach and penetrate the egg within 24 hours of ovulation.
- Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell successfully fuses with the egg, forming a zygote.
B. Implantation
- The zygote begins to divide rapidly, forming a blastocyst.
- Around 6-10 days post-fertilization, the blastocyst implants in the uterine wall.
- This marks the beginning of pregnancy from a clinical perspective.
II. Fetal Development: A Trimester-by-Trimester Guide
A. First Trimester (Weeks 1-13)
Weeks 1-4:
- Implantation occurs
- The primitive streak forms, determining the embryo's body axis
- Neural tube development begins
Weeks 5-8:
- Major organs start to form (organogenesis)
- The heart begins to beat around week 6
- Brain and spinal cord continue to develop
Weeks 9-13:
- Fetus measures about 3 inches long by week 13
- External genitalia begin to differentiate
- Limb movement begins
B. Second Trimester (Weeks 14-26)
Weeks 14-17:
- Rapid growth occurs
- Lanugo (fine body hair) appears
- Fetal movement may be felt (quickening)
Weeks 18-21:
- Vernix caseosa (waxy coating) covers the skin
- Eyebrows and eyelashes form
- Maternal perception of fetal movement increases
Weeks 22-26:
- Fingernails and toenails develop
- Lungs begin producing surfactant
- Startle reflex develops
C. Third Trimester (Weeks 27-40)
Weeks 27-31:
- Rapid brain growth
- Eyes can open and close
- Immune system continues to develop
Weeks 32-36:
- Bones fully developed but still soft
- Rapid weight gain
- Most organs are fully functional
Weeks 37-40:
- Considered full-term
- Final organ maturation occurs
- Fetus typically assumes head-down position for birth
III. Maternal Physiological Changes During Pregnancy
A. Cardiovascular System
- Cardiac output increases by 30-50%
- Blood volume increases by 40-50%
- Heart rate increases by 10-15 beats per minute
B. Respiratory System
- Oxygen consumption increases by 20-30%
- Tidal volume increases
- Respiratory rate may slightly increase
C. Endocrine System
- Placenta produces hormones (hCG, estrogen, progesterone)
- Thyroid gland enlarges, increasing hormone production
D. Gastrointestinal System
- Decreased gastric motility
- Increased risk of gastroesophageal reflux
- Altered intestinal absorption
E. Urinary System
- Increased glomerular filtration rate
- Increased urinary frequency
IV. Prenatal Care and Monitoring
A. Regular Check-ups
- First trimester: Monthly visits
- Second trimester: Bi-monthly visits
- Third trimester: Weekly visits from week 36
B. Routine Tests and Screenings
First Trimester:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood type and Rh factor
- Rubella immunity
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Second Trimester:
- Glucose challenge test for gestational diabetes
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test
- Anatomical ultrasound (around 20 weeks)
Third Trimester:
- Group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening
- Non-stress tests (if indicated)
C. Genetic Screening Options
- Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT)
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
- Amniocentesis
V. Nutrition and Lifestyle During Pregnancy
A. Nutritional Requirements
- Increased caloric intake (about 300 extra calories per day)
- Increased protein intake (70-100 grams per day)
- Essential micronutrients: Folic acid, Iron, Calcium, Vitamin D
B. Exercise Recommendations
- Moderate exercise (150 minutes per week) is generally safe
- Avoid high-impact or contact sports
- Swimming and prenatal yoga are excellent options
C. Substances to Avoid
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
- Certain medications (consult healthcare provider)
- Raw or undercooked meats and fish
- High-mercury fish
VI. Common Pregnancy Complications
A. Gestational Diabetes
- Affects 2-10% of pregnancies
- Managed through diet, exercise, and sometimes insulin
B. Preeclampsia
- Characterized by high blood pressure and protein in urine
- Occurs in 5-8% of pregnancies
- Can lead to serious complications if untreated
C. Placenta Previa
- Low-lying placenta covering the cervix
- Occurs in about 1 in 200 pregnancies
D. Preterm Labor
- Labor beginning before 37 weeks gestation
- Risk factors include multiple pregnancies, cervical insufficiency
VII. Preparing for Birth
A. Birth Plan Considerations
- Pain management preferences
- Delivery method preferences
- Immediate postpartum care wishes
B. Signs of Labor
- Regular contractions
- Rupture of membranes ("water breaking")
- Bloody show
C. Stages of Labor
- First Stage: Labor onset to full dilation
- Second Stage: Full dilation to birth
- Third Stage: Delivery of placenta
VIII. Postpartum Care
A. Physical Recovery
- Uterine involution
- Lochia (postpartum vaginal discharge)
- Breast changes and lactation
B. Emotional Well-being
- Postpartum mood disorders screening
- Support systems importance
C. Newborn Care
- Breastfeeding support
- Routine check-ups and vaccinations
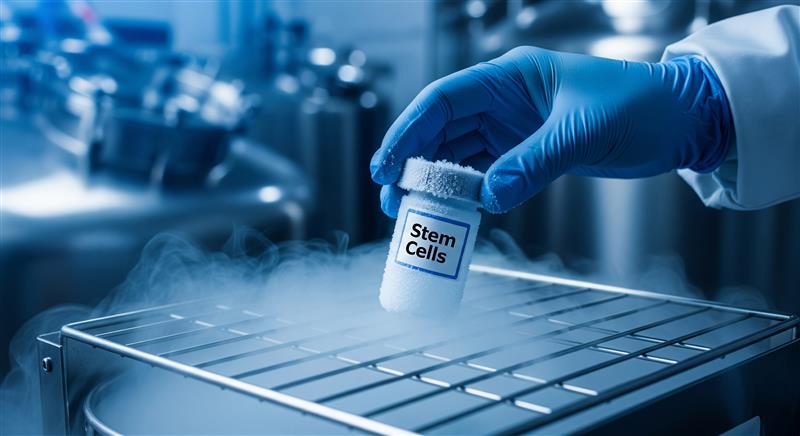
IX. Future Health Considerations: Cord Blood Banking
As you prepare for your child's birth, it's crucial to consider long-term health options. Cord blood banking, offered by companies like Cryoviva Life Sciences, provides a unique opportunity to preserve potentially life-saving stem cells from your baby's umbilical cord blood.
A. What is Cord Blood?
Cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. It's rich in hematopoietic stem cells, which can develop into various types of blood cells.
B. Potential Uses of Cord Blood Stem Cells
- Treatment of blood disorders
- Immune system disorders
- Metabolic disorders
- Ongoing research for future applications
C. The Banking Process
- Collection: Painless collection after cord clamping
- Processing: Stem cells are isolated and cryopreserved
- Storage: Long-term storage in specialized facilities
By choosing to bank your baby's cord blood with a reputable provider like Cryoviva Life Sciences, you're investing in a potential health resource for your child's future.












 Enquiry
Enquiry
 Email
Email Phone
Phone
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp