Gestational Diabetes: Causes, Prevention, And Management
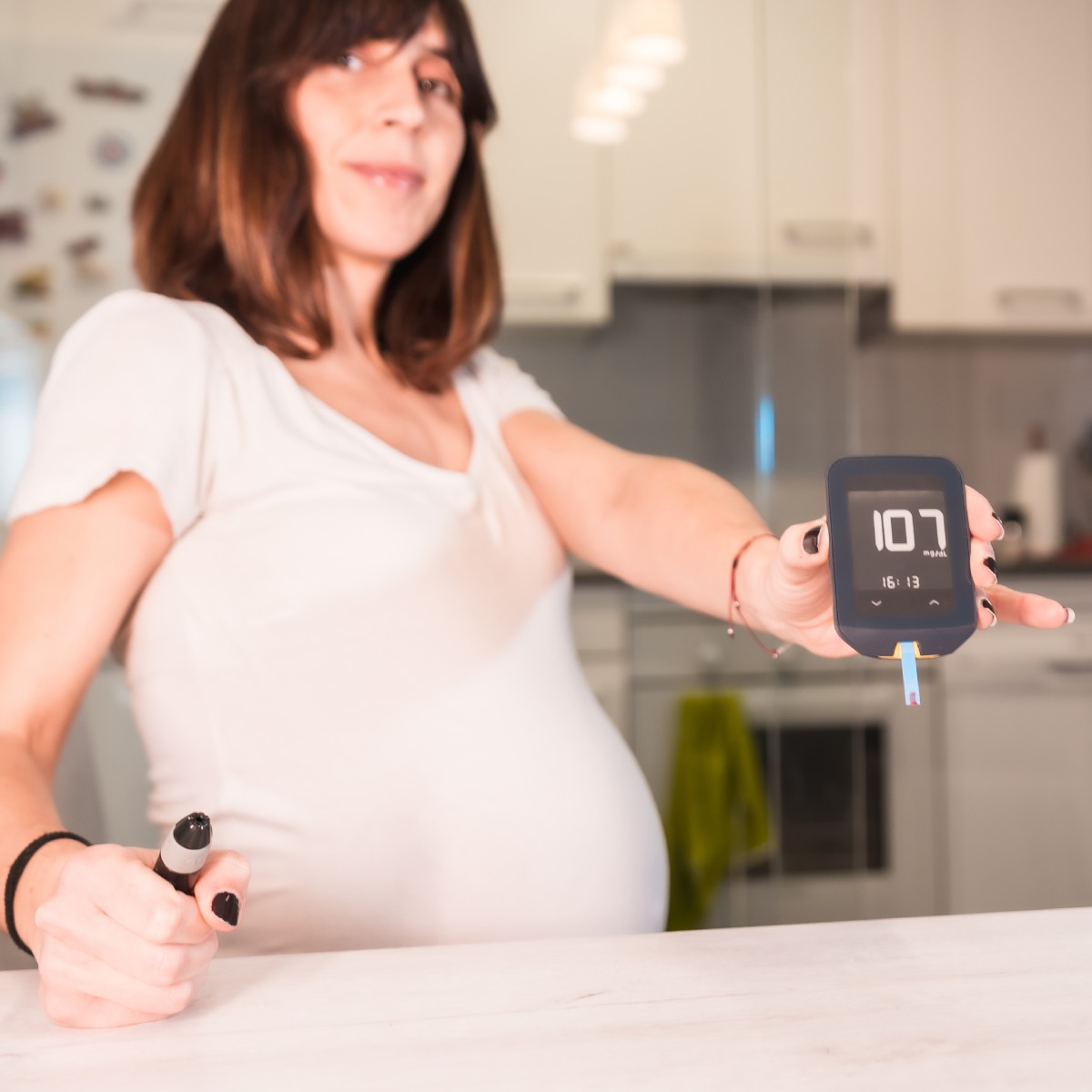

Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that usually occurs during pregnancy. In this condition, the blood glucose in the pregnant woman elevates above normal, leading to affect on both the mother as well as the baby. According to research, 1 in 7 pregnancies in the world is affected by gestational diabetes.
The primary symptoms of gestational diabetes are excessive thirst, frequent urination, dry mouth, genital itching, blurred vision, and more. If you have gestational diabetes during pregnancy, then this blog is for you. In this blog, we will share the major causes, prevention, and management of gestational diabetes.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes usually occurs when your body is incapable of producing sufficient insulin during pregnancy. Here are the major causes of gestational diabetes:
- Hormonal Changes:
During pregnancy, your placenta produces hormones that can hinder insulin action, a hormone responsible for blood sugar regulation.
- Insulin Resistance:
As the gestation period progresses, the body cells become less responsive to insulin. This resistance will increase insulin needs in pregnant women and can result in high blood sugar levels.
- Pancreatic Function:
Another cause is when your pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to meet body demand during pregnancy, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Prevention and Management
Before planning your pregnancy, you may prevent gestational diabetes with simple lifestyle changes. Proper GD management can minimize complications for both the mother and the baby. Let’s see how:
- Follow a Healthy Diet:
Avoid refined carbohydrates like white bread, candy, and cold drinks; instead, consume healthy food options like whole-grain bread, fruits, and vegetables.
- Eat Small Meals:
Split your meal into small parts or consume low-carb snacks throughout the day (in between 2-4 hours) instead of having a large meal at a time.
- Exercise:
Stay active throughout your pregnancy. You can include activities like walking, cycling, using stairs, yoga, and other less strenuous exercises for 4-5 days a week (around 30 minutes a day).
- Monitor Your Glucose Level:
Track your glucose level frequently to check whether the measures you have taken to prevent gestational diabetes are working or not.
Note: Women with gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. So, share your diagnosis with your healthcare provider.
Gestational Diabetes: Dos & Don’ts During Pregnancy
Besides the above prevention and management, there are some pregnancy tips that you need to follow:
Dos:
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly.
-
Eat a balanced diet with vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
-
Choose low glycemic index foods.
Don’ts:
- Avoid sugary foods and drinks.
-
Don’t skip meals.
-
Limit processed and high-carb foods.
Wrapping Up
Consequently, the risk of gestational diabetes can be reduced by following a low-carb diet, regular exercise, and regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels. However, if you think you might develop gestational diabetes, you should consult your primary healthcare provider at your next pregnancy checkup.
We understand your concern about a healthy pregnancy; however, have you ever thought of your baby’s future when it is linked to life-threatening diseases? If not, then consider stem cell banking at Cryoviva Life Sciences with state-of-the-art technology. Partnering with us, you can use stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes and keep your family healthy.










 Enquiry
Enquiry
 Email
Email Phone
Phone
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp