Current challenges facing while cord blood banking

You may be aware of many of the advantages of cord blood banking. With the numbers benefits of Cord Blood Banking, there are some challenges that come with advantages. The challenges are based on the different locations and include high cost, limited availability of the samples or some ethical concerns. Let us look at these challenges in detail.
Challenges Faced while Cord Blood Banking
Here are some of the common challenges faced in cord blood banking.
1. Cost and accessibility
The first challenge comes when the cost of cord blood banking is too high, and the stem cell facility doesn’t have a wide network. The usual pricing for collecting and processing is from Rs. 1,00,000 to Rs. 3,00,000 in private banks. The yearly storage fee is average Rs. 60,000.
Public banking is usually free of cost, enabling anyone to use the facility. However, very few public banks exist, and they may not have the matching cord blood unit for the patient in need. Furthermore, some countries have few to zero public cord blood banks, making it difficult for people to obtain this crucial resource.
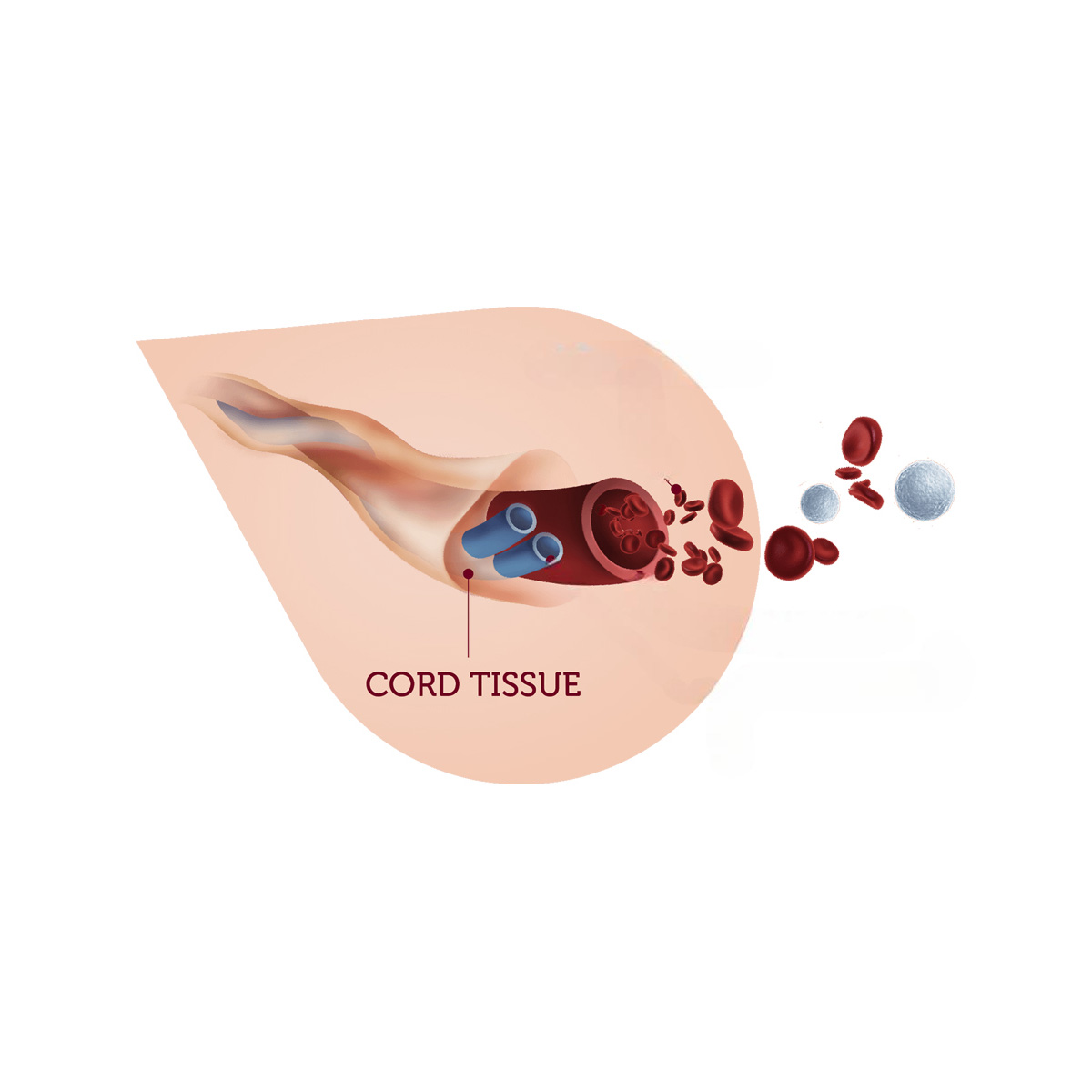
2. Low volume and cell count
With the process, the blood from the umbilical cord and placenta is limited to 40 to 150 ml, which is considered less than what is required for the transplantation process. Additionally, the storage requires a temperature of less than 170 degrees celsius, which is difficult for all healthcare organizations.
3. Informed Consent and Autonomy
The practice of cord blood banking involves collecting and preserving stem cells from babies' umbilical cords. Parents must decide whether to bank their child's cord blood for potential future usage. Informed consent is critical in this situation. Healthcare practitioners must ensure that parents understand the entire procedure, including risks, benefits, and alternatives. It is difficult to strike a balance between wanting to protect the child's health and respecting parental autonomy.
4. Ownership and Access
Cord blood banks keep samples for private or public usage. Private banks serve particular families, but public banks accept donations from anybody in need. The issue of ownership arises: Who owns the cord blood—the family, the child, or society? Legal frameworks differ between countries. Some claim that cord blood is a community resource, similar to blood donation. Others emphasise individual ownership, like consider a case in which a sibling requires a stem cell transplant, and the stored cord blood matches. Hence, it is difficult to set-up ownership.
5. Quality Control and Testing Issues
When it comes to cord blood banking, quality control and testing are important to ensure the sample meets the quality standards when required. However, challenges might arise, such as sample contamination or infectious disease screening, which affects the usability and efficiency of the cord blood.
Final Words
Cord blood banking holds great medical potential but faces significant challenges. High costs must be managed. The availability of public banks may help patients when in need. Increased efforts are required to overcome these barriers and make cord blood banking more accessible and effective. Cryoviva ensures the safe collection and storage of your sample. The team ensures that you are well informed about all the ethical and legal guidelines.










 Enquiry
Enquiry
 Email
Email Phone
Phone
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp