Baby Cord Blood Stem Cell Research and Its Life Benefits
Stem cells hold incredible promise for medicine with the potential to repair, replace, or rescue damaged cells and deliver targeted therapies. While there are challenges with using embryonic and fetal stem cells, stem cells from the umbilical cord offer a practical alternative.
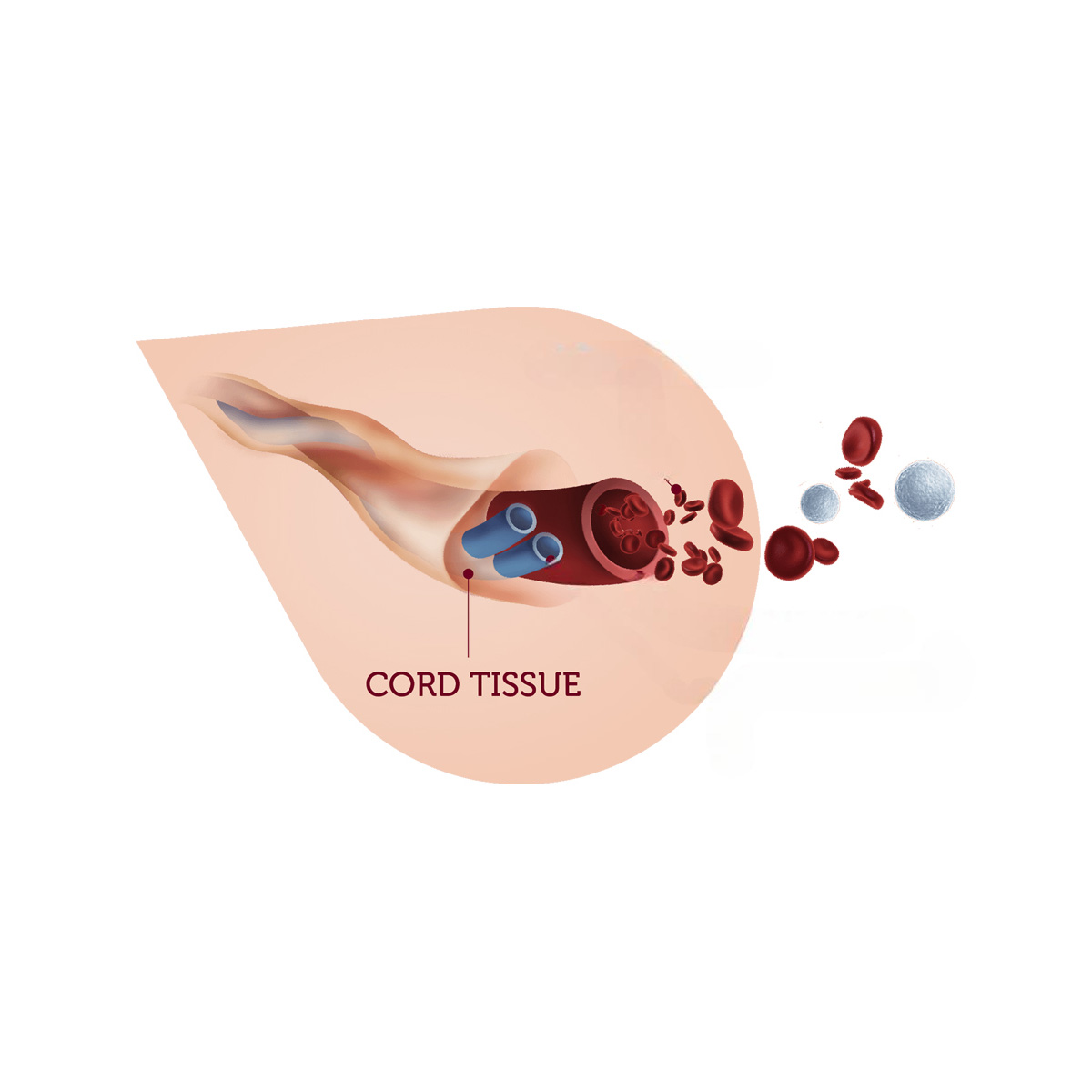
These cells, found in the umbilical cord blood, amnion, placenta, and other parts of the cord, are easily accessible and cost-effective. They are also "multipotent," meaning they can become various types of cells. Next, let us discuss the baby cord blood stem cells and their current research.
What is Umbilical Cord Blood Composed of?
The cellular component of UCB consists mostly of lymphocytes and monocytes. It has a comparable B-lymphocyte population, a lower absolute number of T-lymphocytes (CD3+), and a greater CD4+/CD8+ ratio than APB. UCB also has more NK cells but less CD56+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (18). In comparison to adult cell sources, UCB is more immature, with a higher proportion of immature T-lymphocytes (CB45RA+) and less mature memory T-lymphocytes (CD45RO+). UCB cells also produce lower absolute quantities of cytokines than adult cell sources. Anti-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-10 are more prevalent in UCB mRNA than proinflammatory cytokine IL-2.
How is Stem Cell Research helpful?
Researchers use human stem cells in a variety of fundamental and clinical research applications. They are:
Understand the development of human organs: Embryonic stem cells have been employed to investigate the precise signals and differentiation processes required for the creation of numerous organs.
Cell-based therapies: This is possibly the most promising application of human stem cells. They produce cells and tissues suitable for cell-based therapy.
Brain Injury: Although the reparative process appears to begin, significant recovery is rare in adults, indicating a lack of robustness. Recent research in stroke-affected mice suggests that administering medications to boost stem cell division rate and direct the survival and differentiation of newly generated cells may be effective.
Spinal cord injury: Recently, substantial research has been conducted to treat spinal cord injuries. Scientists cured a patient with a spinal cord injury by separating adult stem cells from umbilical cord blood and injecting them into the injured region of the spine.
Heart Disease: Adult stem cell treatment has been shown in several clinical trials to be safe for treating cardiac disease. However, none of these studies have demonstrated efficacy till date. The use of patients' own bone marrow-derived stem cells and peripheral blood-derived stem cells is becoming increasingly popular.
Controversies in Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research is faced with ethical issues since the stem cells with the greatest potential for study must be extracted from human embryos as young as a few days old. The most notable issue in stem cell research has been Hwang's claim to have cloned a dog. Hwang's work was able to provide an alternative to using actual human embryos by cloning numerous human embryos, hence reducing the demand for additional embryos. Hwang claimed to have successfully cloned 30 human embryos, however, these claims have already been proven to be false.
Unfortunately, the usage and research of embryonic stem cells is currently shrouded by ethical concerns. Adult stem cells are special in that they can be isolated, researched, or modified without damaging the donor. There are currently various difficulties in using adult stem cells as a therapeutic. For starters, a paucity of stem cell markers makes it difficult to identify the majority of adult stem cells. In vitro, techniques for altering adult stem cell populations are frequently poorly characterized.
Final Thought
Stem cells offer interesting treatment alternatives for diseases that are currently thought to be incurable. However, due to the high peri- and post-transplant morbidity and mortality, additional research and trials are needed to enhance and optimize conditioning regimens and supportive care methods. We think that by sponsoring stem cell research, we will be able to witness new therapeutic horizons in the form of organ development and replacement of lost tissue such as hairs, teeth, retina, and cochlear cells.
Cryoviva offers world-class banking facilities related to stem cell preservation and you can connect with them to know more about benefits of stem cell and recent development in the regenerative medicine field which makes stem cells precious little cells.














 Enquiry
Enquiry
 Email
Email Phone
Phone
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp